Apache Kafka and MQTT are a perfect combination for many IoT use cases. This blog series covers the pros and cons of both technologies. Various use cases across industries, including connected vehicles, manufacturing, mobility services, and smart city are explored. The examples use different architectures, including lightweight edge scenarios, hybrid integrations, and serverless cloud solutions. This post is part four: Mobility Services and Transportation.

Apache Kafka + MQTT Blog Series
The first blog post explores the relation between MQTT and Apache Kafka. Afterward, the other four blog posts discuss various use cases, architectures, and reference deployments.
- Part 1 – Overview: Relation between Kafka and MQTT, pros and cons, architectures
- Part 2 – Connected Vehicles: MQTT and Kafka in a private cloud on Kubernetes; use case: remote control and command of a car
- Part 3 – Manufacturing: MQTT and Kafka at the edge in a smart factory; use case: Bidirectional OT-IT integration with Sparkplug between PLCs, IoT Gateways, Data Historian, MES, ERP, Data Lake, etc.
- Part 4 – Mobility Services (THIS POST): MQTT and Kafka leveraging serverless cloud infrastructure; use case: Traffic jam prediction service using machine learning
- Part 5 – Smart City: MQTT at the edge connected to fully-managed Kafka in the public cloud; use case: Intelligent traffic routing by combining and correlating 3rd party services
Subscribe to my newsletter to get updates immediately after the publication. Besides, I will also update the above list with direct links to this blog series’s posts as soon as published.
Use Case: Mobility as a Service (MaaS) and Transportation
Transportation is changing significantly these days. Mobility Services – often called Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) – is a type of service that through a joint digital channel enables users to plan, book, and pay for multiple types of mobility services.

The concept describes a shift away from personally-owned modes of transportation and towards mobility provided as a service. This is enabled by combining transportation services from public and private transportation providers through a unified gateway that creates and manages the trip, which users can pay for with a single account. Users can pay per trip or a monthly fee for a limited distance. The key concept behind MaaS is to offer travelers mobility solutions based on their travel needs. Specialist urban mobility applications are also expanding their offerings to enable MaaS, such as Transit, Uber, and Lyft.
Travel planning typically begins in a journey planner. For example, a trip planner can show that the user can get from one destination to another by using a train/bus combination. The user can then choose their preferred trip based on cost, time, and convenience. At that point, any necessary bookings (e.g. calling a taxi, reserving a seat on a long-distance train) would be performed as a unit. It is expected that this service should allow roaming, that is, the same end-user app should work in different cities, without the user needing to become familiar with a new app or to sign up for new services.
As you can hopefully already imagine, plenty of innovative new use cases are possible by combining Apache Kafka and MQTT for MaaS. And most of these scenarios require data integration and data processing at scale in real-time.
Architecture: MQTT and Kafka for Mobility Services
Mobility services are often separated from other core IT infrastructure. MaaS – as the term says – is just consumed as a service. Hence, most mobility services I have seen run in the cloud. The following diagram shows an intelligent navigation service built with MQTT, Kafka, and Machine Learning:
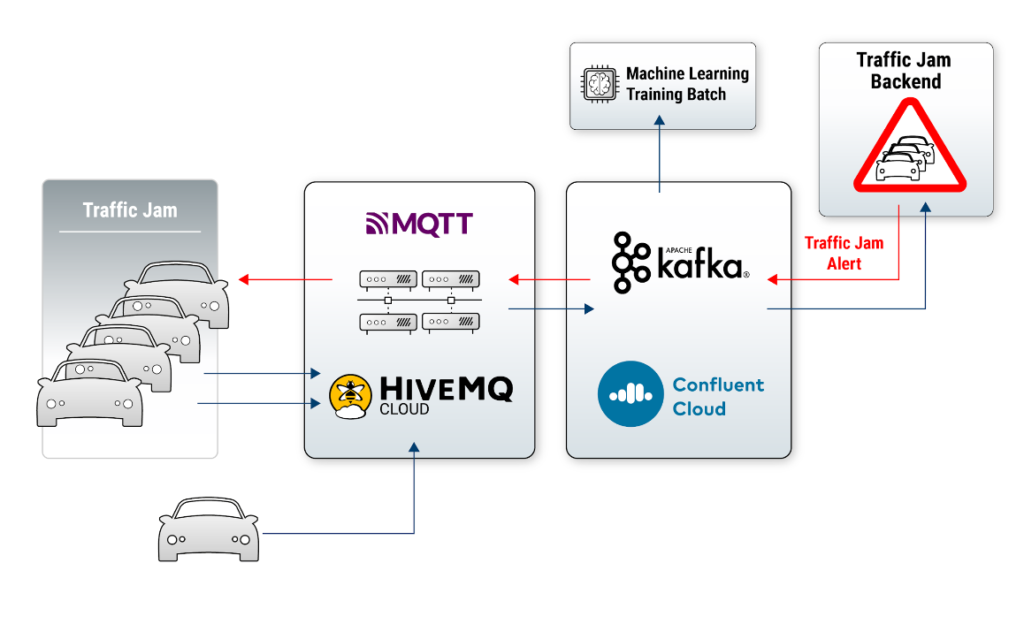
A few notes on the architecture:
- As mobility services connect to moving vehicles, smartphones, or other things, the cloud is perfect. No need to operate the infrastructure. Just focus on building applications.
- Many mobility services integrate other 1st or 3rd party services. For instance, there is no need to build yet another mapping service. If you need one for building your innovative new application, just embed HERE Technologies (that actually provides a public Kafka interface as the preferred integration option instead of HTTP!) or any other available mapping service.
- Regional services with low latency are often very relevant for mobility services. Hence, multiple MQTT and Kafka clusters are the norm, not an exception.
Let’s take a look at some real-world examples for cutting-edge mobility services in the transportation industry.
Example: Cloud Ecosystem for Next-Generation Mobility @ ZF
ZF Friedrichshafen AG is a global automotive supplier that enables vehicles to see, think, and act. With a broad range of systems for passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and industrial technology, ZF offers comprehensive solutions for established vehicle manufacturers as well as newly emerging transport and mobility service providers.
ZFs Connectivity Suite enables new business models for mobility as a service (MaaS) and transportation as a service (TaaS). The ProCV gateway device allows each vehicle to communicate using MQTT. The gateway provides a secure and reliable channel for transferring telemetry data from the car to the cloud and remote commands from the cloud to each vehicle.
Applications can exchange data such as real-time positioning information, remote commands to the vehicle, and vehicle-generated alerts. Some possible use cases:
- Remote diagnostics for technical insight & management of vehicle performance
- Fleet monitoring
- Secure & reliable middleware between connected vehicles & cloud services
Read the case study from HiveMQ for more details about ZF’s IoT gateway.
Example: Real-Time Traveler Information @ Deutsche Bahn
Deutsche Bahn (the German railway) has a very complex network of short-distance and long-distance trains. Hence, delays and cancellations are common, not an exception. Hence, at least the traveler information should work well to send real-time notifications to customers.
For that reason, Deutsche Bahn has built a single source of truth traveler information platform with Confluent:

The mobility service integrates via Kafka with many legacy and modern applications. The mobile app shows real-time status updates about each train. While train delays and cancellations cannot be avoided completely, the app at least allows you to get to a lounge or grab a coffee if the delay is more than just a few minutes. I use the app every week myself and can confirm that the customer experience improved significantly.
Not every interface is or will be real-time. Kafka helps!
Fun fact: The first proof of concept to build this traveler information app used a traditional messaging queue. In theory, this is is sufficient as you “just” need to send status updates in real-time to the mobile app. Unfortunately, a few issues came up quickly:
- Not every interface is real-time! In addition to messaging sources such as JMS or MQTT, the platform needed to integrate with databases, files, web services, and other legacy systems. Hence, data integration and is a key piece of the puzzle.
- Data storage is important to handle backpressure and decouple applications. Slow consumers fall behind. Analytics workloads take data in batches, not in real-time. Web applications consume specific events via request-response queries.
- Sending events from A to B is just part of the problem! The real added value comes by correlating the data from streaming and non-streaming applications and databases in real-time. Kafka-native Stream processing frameworks such as Kafka Streams or ksqlDB help to process data in motion.
For the above reasons, Deutsche Bahn re-started their proof of concept. Their existing project used different frameworks for messaging, caching, integration, and processing. This setup was replaced with Kafka. Kafka Connect integrates applications and databases. Kafka Streams processes the data in motion. The Kafka storage handles backpressure and slow consumers. All of this is built into Kafka out-of-the-box. And it scales much better. Today, the traveler information system is live and creates a much better customer experience.
Find more details about the traveler information system from Deutsche Bahn in their Confluent blog post.
Kafka + MQTT = Mobility Services and Transportation
In conclusion, Apache Kafka and MQTT are a perfect combination for mobility services and transportation. Follow the blog series to learn about use cases such as connected vehicles, manufacturing, mobility services, and smart city. Every blog post also includes real-world deployments from companies across industries. It is key to understand the different architectural options to make the right choice for your project.
What are your experiences and plans in IoT projects? What use case and architecture did you implement? Let’s connect on LinkedIn and discuss it! Stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter.






